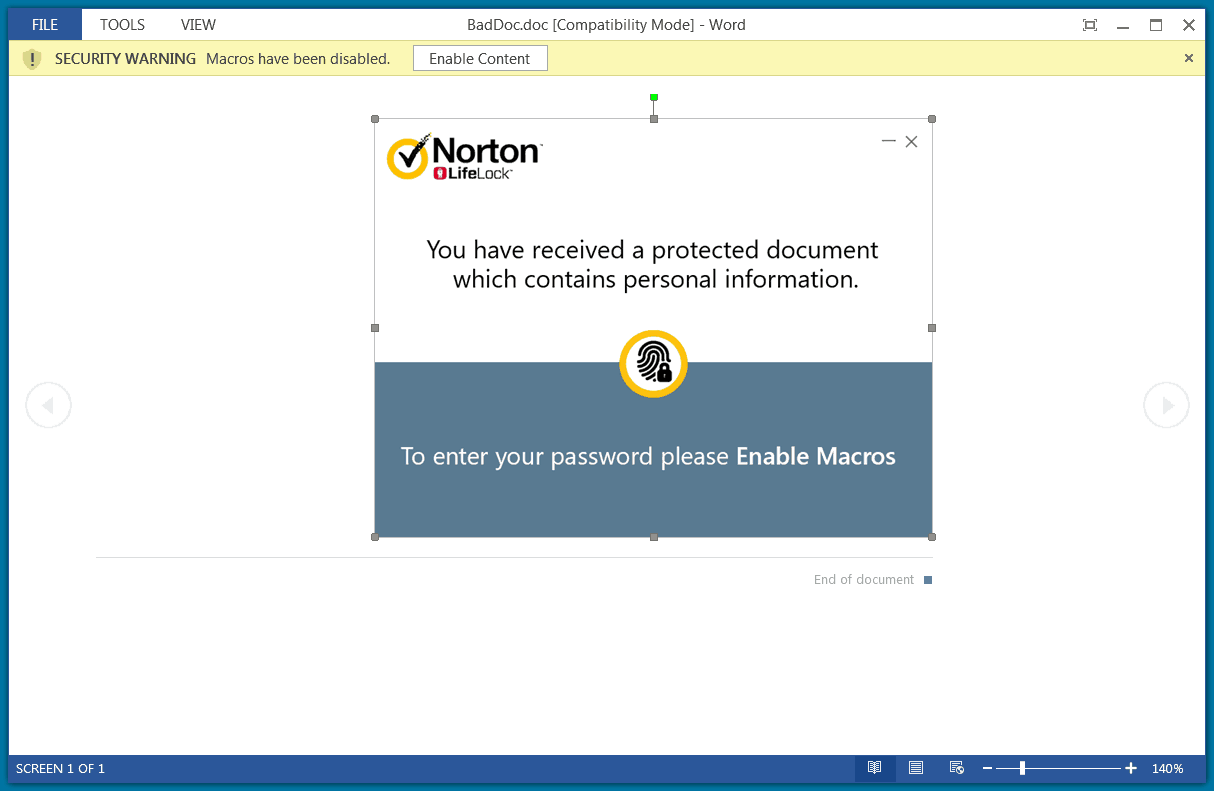
Attackers leveraging popular names to gain trust among users is common in cybercrime. Here, they’re just using it to make enable macros by the user, so they could dump a RAT and exploit further. The campaign starts with a phishing email that contains a malicious document titled as Norton LifeLock. This claims to have personal information if the user and asks him to check by opening it by a password. The password is mostly provided within the email, alongside the document.
The Macro enabling
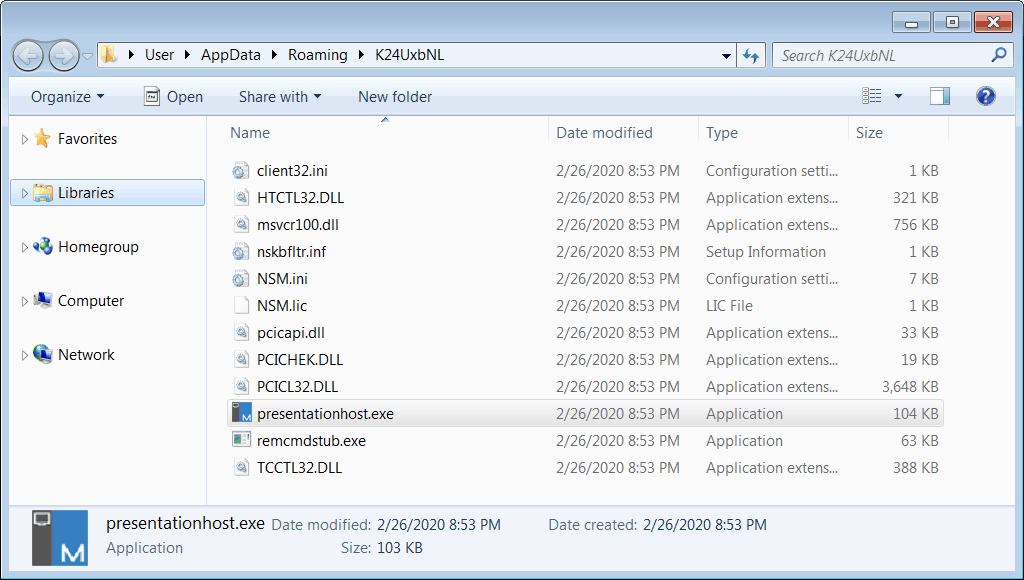
Passwords need macros. And as Microsoft disables macros by default in its Office suite, the attacker prompts users to enable macros to view information, via the document. And when opened by given password, it downloads a Remote Access Trojan called NetSupport Manager. This payload seems legitimate and has administrator access to look into clients accounts. This RAT is procured from the domain quickwaysignstx[.]com/view.php and installs using msiexec command in Windows installer. Here, the payload retrieved adds a Powershell script in Windows %temp% folder, all without victim’s notice. This is done to act as a backup for NetSupport Manager. But after the RAT is executed, this Powershell script is removed. The script, even before executing, checks the computer for Antivirus softwares like Avast or AVG. And if found, will not install anything further. But if nothing harm is found, the script then adds a folder with random name and NetSupport Manager files, along with a registry key as ‘HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run. After all, it starts executing and sends information about the system to the attacker. This campaign was first detected by Unit 42 of Palo Alto Networks in January this year. But deep research reveals the campaign is active since November last year and is on a wider scale. Source: Unit 42